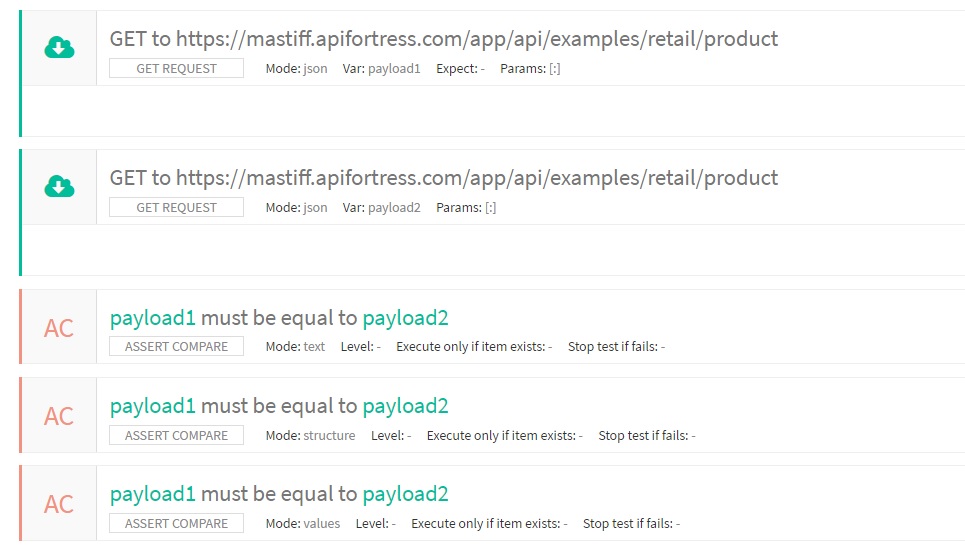
Allows you to compare two payloads in terms of text, structure or values.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression 1 |
Expression |
Yes |
| Expression 2 |
Expression |
Yes |
| Mode |
Text, values, structure |
Yes |
| Level |
error, warning |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
True, false |
No |
Expression 1: the first payload you want to compare.
Expression 2: the second payload you want to compare.
Mode: the comparator you wish to use.
Text compares the text of the two payloads as plain text,
values compares the two payloads regardless the text layout,
structure compares only the structure of the two payloads.
Level: Specifies, when the assertion fails, whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
This assertion is used to check if the element value described by the expression matches a knowledge base of some kind. For example a
US Zipcode or a
US State. This also gives you the ability to write your own regex (regular expression).
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Type |
‘regex’ or ‘US Zipcode’ or ‘US State’ or ‘credit card’ or ‘country codes’ or ‘currency codes’ |
Yes |
| Regex value |
String |
Yes, if type is ‘regex’ |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Type: The data type of the value. The possible values are: ‘regex’, if you want to evaluate the field as a regular expression (specified in regex value); ‘US Zipcode’, checks if the field is a valid US Zipcode; ‘US State’, checks if the field is a valid US State (i.e. ‘NY’); ‘credit card’; checks if the field contains a valid credit card number from the most popular credit cards (i.e. VISA, Mastercard, AMEX); ‘country codes’, checks if the field contains a valid country code (i.e. ‘US’, ‘FR’, ‘DK’); ‘currency codes’, checks if the fields is a valid currency (i.e. ‘USD’, ‘EUR’)
Regex value: Specify the regular expression you want to use for checking the expression.
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Examples:
| <assert-matches expression=”data.zipcode” type=”us_zipcodes”/> |
| <assert-matches expression=”data.state” type=”us_states”/> |
| <assert-matches expression=”data.name” type=”regex” value=”[hc]?at”/> |
| <assert-matches expression=”data.credit” type=”creditCard”/> |
| <assert-matches expression=”data.country” type=country_codes”/> |
| <assert-matches expression=”data.code” type=”currency_codes”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the element value described by the expression is equal to a specific value. A direct one-to-one comparison.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Value |
String |
Yes |
| Type |
‘integer’ or ‘float’ |
No |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Value: The value we want to compare the expression to.
Type: The data type of the value. This attribute is optional. If no type is defined the values will be compared as strings. If the type is set the values will evaluated with the chosen comparator (ex: ‘integer’ as a whole number, ‘float’ as a decimal number).
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Examples:
| <assert-equals expression=”data.code” value=”500″/> |
| <assert-equals expression=”data.code” value=”500″ type=”integer”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the element described by the expression matches at least one item from a given list. For example, the category of a product is one of the approved categories such as
men,
women, or
children.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Value |
String |
Yes |
| Type |
‘integer’ of ‘float’ |
No |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Value: The value we want to compare the expression to.
Type: The data type of the value. This attribute is optional. If no type is defined the values will be compared as strings. If the type is set the values will evaluated with the chosen comparator (ex: ‘integer’ as a whole number, ‘float’ as a decimal number).
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Examples:
| <assert-in expression=”data.type” value=”[‘paperbook’,’ebook’]”/> |
| <assert-in expression=”data.price” value=”[5.50,7,9.79]” type=”float”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the element value described by the expression is less than a proposed value. The values can be compared as a
string or
number.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Value |
String |
Yes |
| Type |
‘integer’ or ‘float’ |
No |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Value: The value we want to compare the expression to.
Type: The data type of the value. This attribute is optional. If no type is defined the values will be compared as strings. If the type is set the values will evaluated with the chosen comparator (ex: ‘integer’ as a whole number, ‘float’ as a decimal number).
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Examples:
| <assert-less expression=”data.code” value=”4503″/> |
| <assert-less expression=”data.code” value=”4503″ type=”integer”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the element value described by the expression is greater than a proposed value. The values can be compared as a
string or
number.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Value |
String |
Yes |
| Type |
‘integer’ or ‘float’ |
No |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Value: The value we want to compare the expression to.
Type: The data type of the value. This attribute is optional. If no type is defined the values will be compared as strings. If the type is set the values will evaluated with the chosen comparator (ex: ‘integer’ as a whole number, ‘float’ as a decimal number).
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Examples:
| <assert-greater expression=”data.code” value=”4503″/> |
| <assert-greater expression=”data.code” value=”4503″ type=”integer”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the element described by the expression contains a specific substring. For example, to test the word
Uber is in Uber’s product names (
UberX, UberBlack, UberPool).
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Value |
String |
Yes |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Value: The value we want to compare the expression to.
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Examples:
| <assert-contains expression=”data.url” value=”domain.com”/> |
| <assert-contains expression=”data.id” value=”${id}”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the element described by the expression exists. The presence of the element, even empty, is enough to consider it a valid assertion.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Example:
| <assert-exists expression=”data.id”/> |
This assertion is used to check if the value of the element defined by the expression belongs to a specific type. This is one of the more commonly used assertions because it can be used to verify various things such as whole numbers, email addresses, phone numbers, URLs, and so forth.
Parameters:
| Name |
Type/Value |
Required |
| Expression |
Expression |
Yes |
| Type |
‘integer’, ‘float’, ‘url’, ‘boolean’, ‘phone’, ’email’, ‘map’, ‘array’ |
Yes |
| Mode |
‘all’ or ‘one’ |
No |
| Level |
‘error’ or ‘warning’ |
No |
| Modifier |
‘not’ |
No |
| Execute if item exists |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Stop test if fails |
‘true’ or ‘false’ |
No |
| Comment |
String |
No |
Expression: It’s the path to the element we want to operate on (e
x: payload.ProductID). See
Expression for more details.
Type: The data type of the value. The possible values are: ‘integer’, checks if field is an integer value; ‘float’, checks if field is a decimal value; ‘url’, checks if the field is a well formatted url; ‘boolean’, checks if field is a boolean value; ‘phone’, checks if field contains a valid phone number format; ’email’, checks if field is a valid email format; ‘map’, checks if field is a map type; ‘array’, checks if the field is an array
Mode: Specify if all the same elements in the payload should match the assertion (‘all’) or if only one element (‘one’) is enough.
Level: Specify if the assertion fails whether it should be considered an ‘error’ or just a ‘warning.’ A warning will not trigger alerts (such as email or text messages).
Modifier: The assertion is considered verified if it does not pass.
Execute if item exists: The assertion is evaluated only if the element exists. This is useful when the element does not always exist.
Stop test if fails: The test will be immediately stopped if the assertion fails.
Code View Example:
| <assert-is expression=”data.id” type=”integer”/> |

