Legacy Documentation
You're viewing legacy documentation for API Fortress (deployed via an on-premises container).
To view documentation for the new SaaS version of API Fortress — now known as Sauce Labs API Testing and Monitoring (with Sauce Connect tunnels) — see
API Testing on the Sauce Labs Cloud.
Passing data from API Fortress to Atlassian Bamboo allows Bamboo users to include API Fortress test results in their CI/CD process.
Step 1: Generating a Webhook
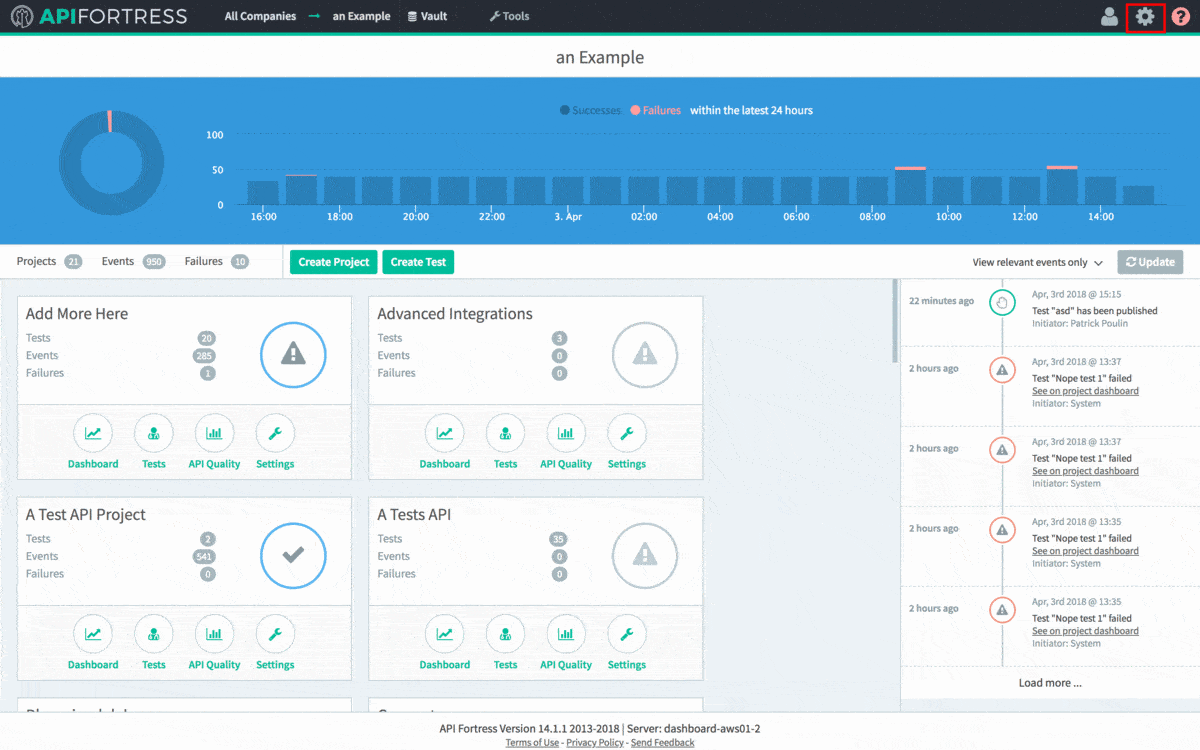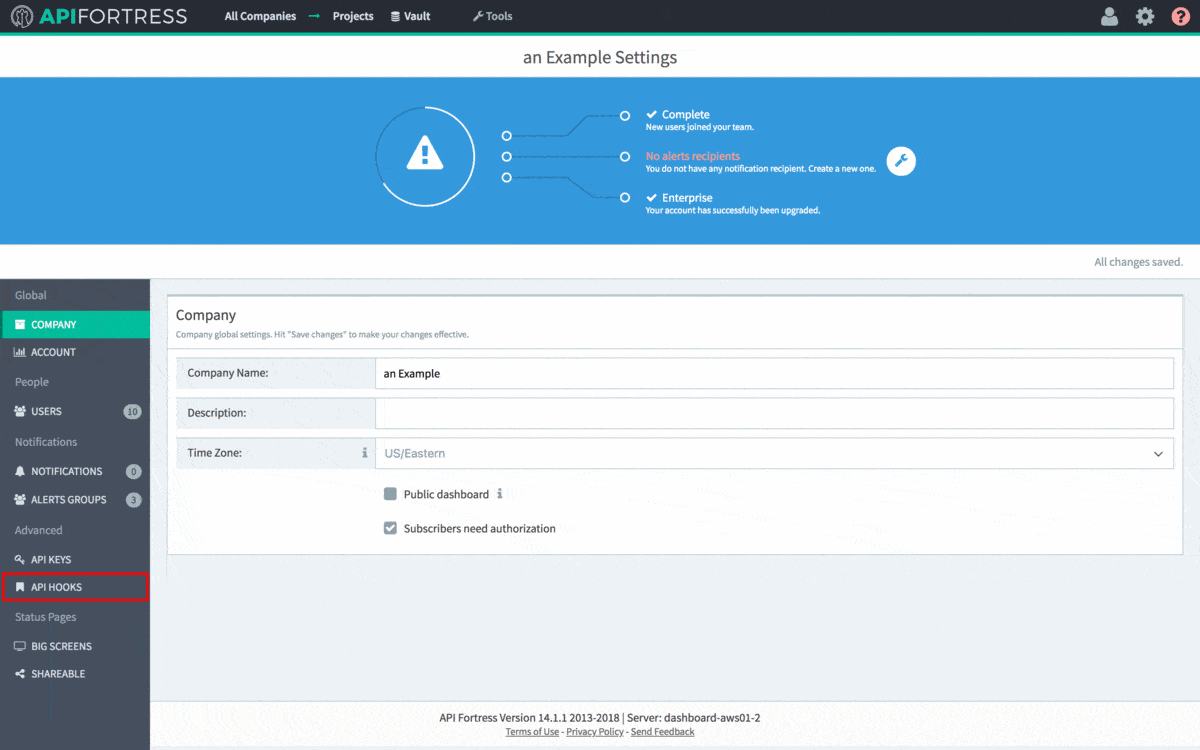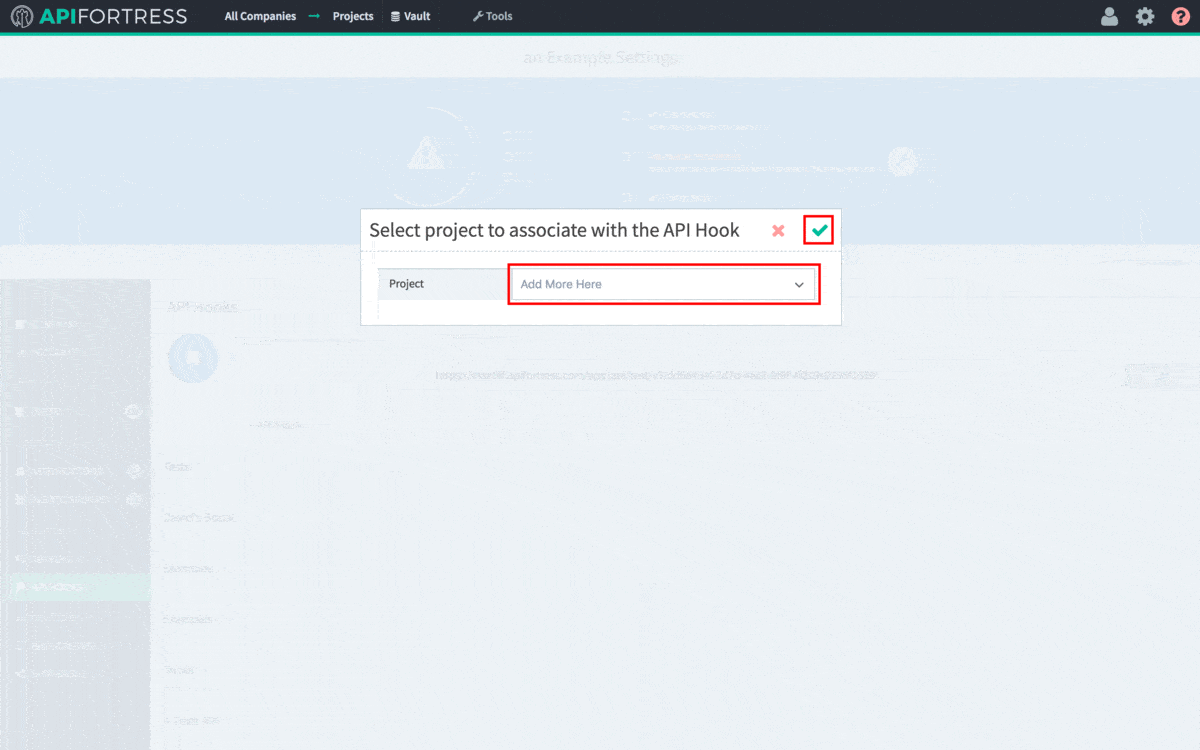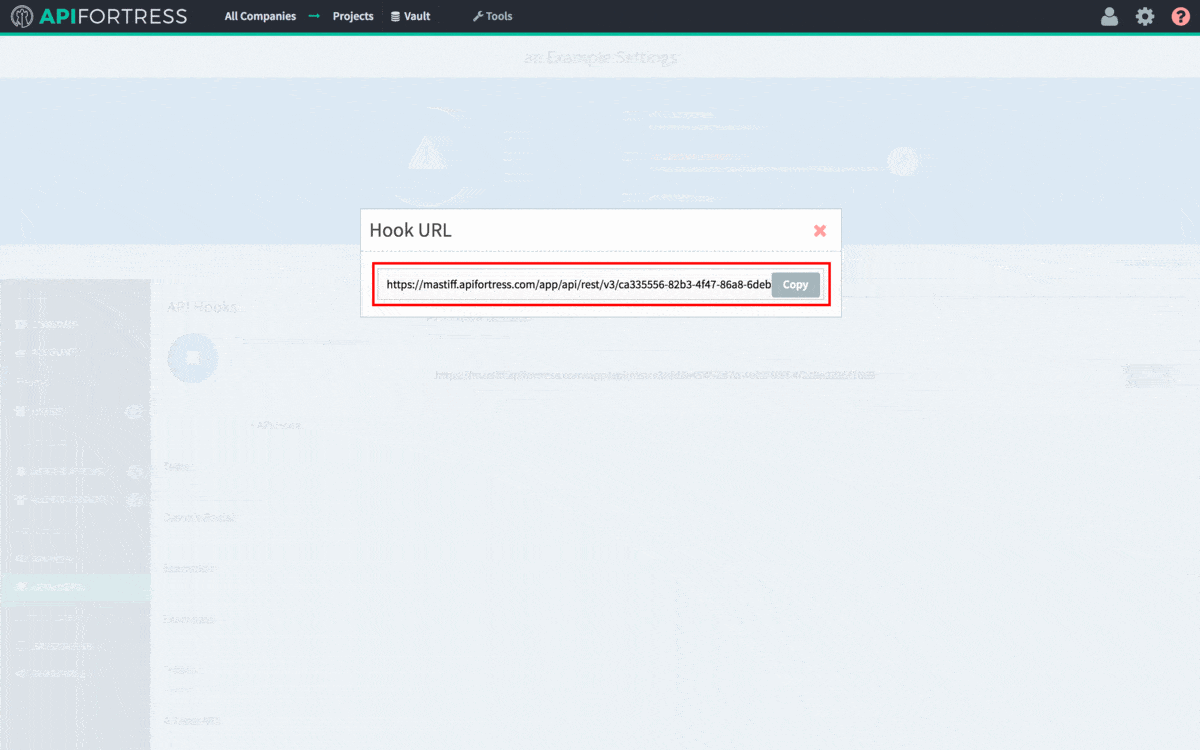
The first step to integrating API Fortress into your CI/CD process is to grab the generated API hook for the project in question. To do so, head to the Settings panel in API Fortress. This view, seen below, can be accessed from anywhere in the application by clicking the
Gear icon in the top right corner of the screen. Please note you need Manager access to generate a webhook. From Settings, click the API Hooks section and generate the hook for your project. The process can be seen in detail in the .gif below.
Step 2: Select or Create a Bamboo Project
After we’ve created our webhook, calling it from within Bamboo is a fairly simple process. First, create a new project in Bamboo. You can also add to an existing project from this screen.
Step 3: Adding an HTTP Call
Next, we need to add an HTTP Call component and enter the webhook we generated. Depending on what you wish the call to API Fortress to trigger, you may append different routing on to the end of the webhook. The API Fortress API Documentation is located
here.

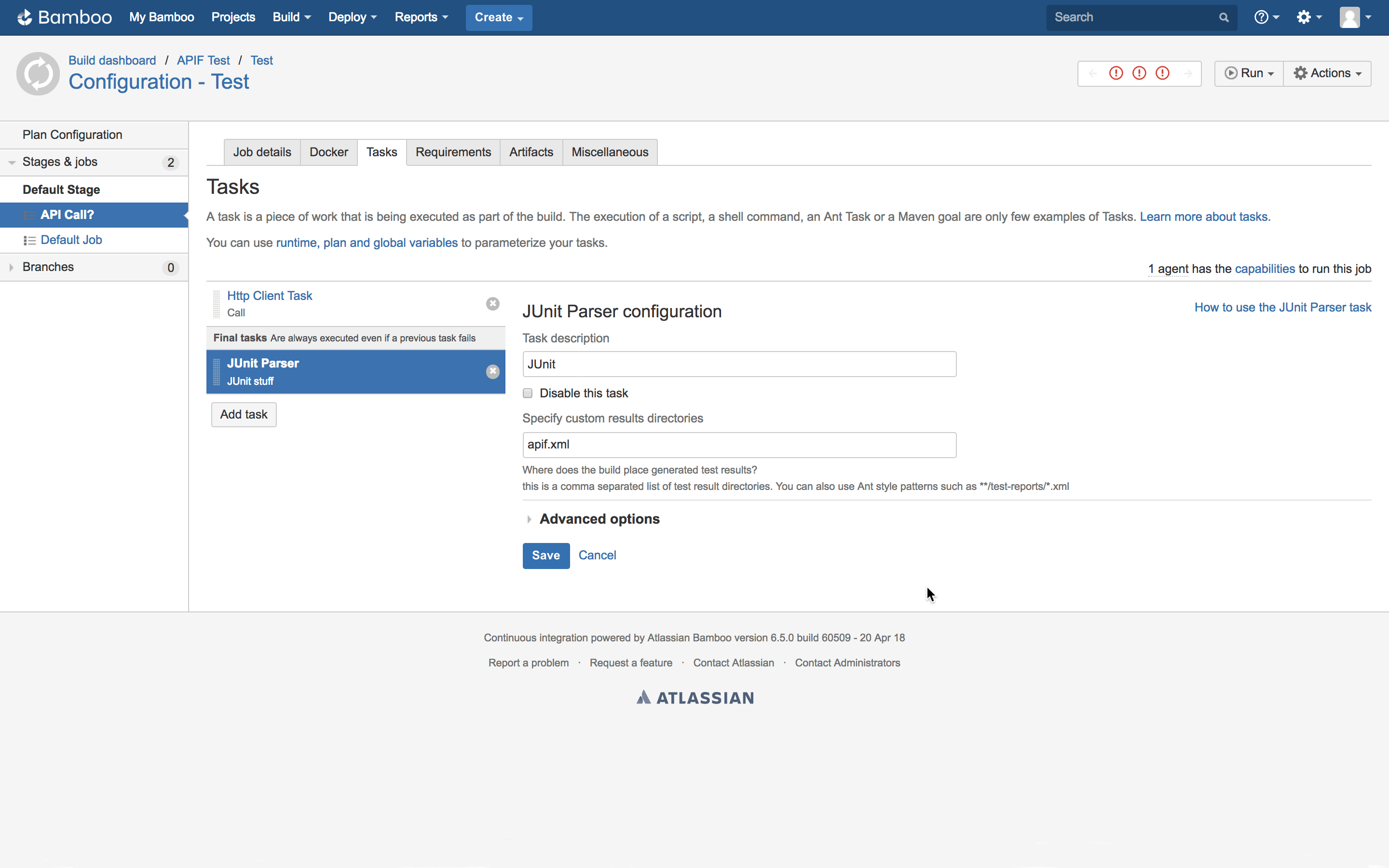
Step 4: Parsing Results
After the request is sent to the API Fortress API, we’ll need to save the JUnit data that’s returned. We do so by adding a JUnit Parser step.
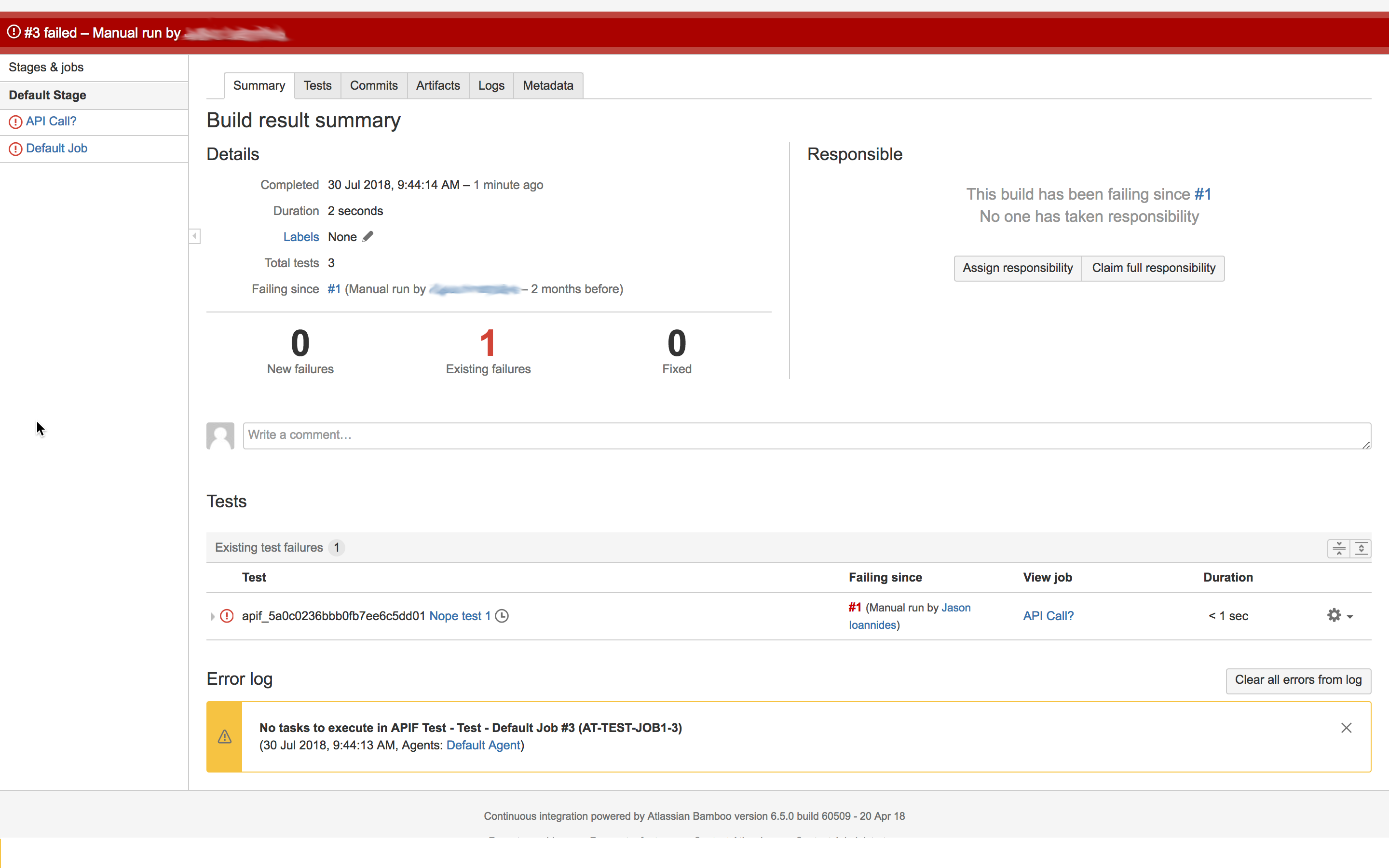
Once the above steps are completed and saved, the build sequence will make a call to API Fortress upon execution, receive the results of the tests, and parse the results.
Keywords: cicd, jenkins, bamboo, microsoft tfs, team foundation server, gitlab ci/cd, travisci



 Once the above steps are completed and saved, the build sequence will make a call to API Fortress upon execution, receive the results of the tests, and parse the results.
Once the above steps are completed and saved, the build sequence will make a call to API Fortress upon execution, receive the results of the tests, and parse the results.
 Keywords: cicd, jenkins, bamboo, microsoft tfs, team foundation server, gitlab ci/cd, travisci
Keywords: cicd, jenkins, bamboo, microsoft tfs, team foundation server, gitlab ci/cd, travisci 